Docker Elasticsearch Container

Are you looking to set up a Elasticsearch container using Docker on your MacOS machine? Look no further! In this article, we'll walk you through the process of creating and configuring a Docker Elasticsearch container, along with Kibana.
Step 1: Create an Environment File
The first step is to create an environment file that will store our database password.
.env
DB_PASSWORD=Password1234This file will be used to set the ELASTIC_PASSWORD environment variable in our Docker container.
Step 2: Create a Docker Compose File
Next, we'll create a Docker compose file that defines our Elasticsearch & Kibana containers.
elk-docker-compose.yml
version: '3.9'
services:
elasticsearch:
# Apple M1 Chip
# platform: linux/amd64
image: elasticsearch:7.17.10
container_name: elasticsearch
restart: always
env_file:
- .env
environment:
bootstrap.memory_lock: "true"
discovery.type: single-node
ES_JAVA_OPTS: -Xms512m -Xmx512m
ELASTIC_PASSWORD: $DB_PASSWORD
xpack.security.enabled: "true"
cluster.name: elasticsearch_cluster
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
ports:
- 9200:9200
- 9300:9300
volumes:
- elasticsearch_datadir:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
networks:
- elk-network
kibana:
# Apple M1 Chip
# platform: linux/amd64
image: kibana:7.17.10
container_name: kibana
restart: always
env_file:
- .env
environment:
KS_JAVA_OPTS: -Xms512m -Xmx512m
ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS: http://elasticsearch:9200
ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME: elastic
ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD: $DB_PASSWORD
XPACK_SECURITY_ENABLED: "true"
ports:
- 5601:5601
volumes:
- kibana_datadir:/usr/share/kibana/data
networks:
- elk-network
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
networks:
elk-network:
driver: bridge
volumes:
elasticsearch_datadir:
kibana_datadir:This file defines two services, elasticsearch and kibana, which uses the official elasticsearch 7.17.10 & kibana:7.17.10 images.
Step 3: Start the Container
Now that we have our environment file and Docker compose file set up, it's time to start the containers! Run the following command:
docker-compose -f elk-docker-compose.yml up -dThis will start the containers in detached mode, meaning they will run in the background.
Step4: Test Elasticsearch Container
Once the containers are running, we can test our Elasticsearch instance using the following commands:
Note: you should have curl command line tool installed locally.
db_password=Password1234
curl -X GET -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/_cat/health?v=true&pretty
curl -X GET -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/_cat/nodes?v=true&pretty
curl -X GET -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/_cat/indices?v=true&prettyNow let us create a new index.
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/product -d '
{
"settings": {
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings":{
"properties": {
"name" : { "type" : "text" },
"description": {"type": "text"},
"uom": {"type" : "text"},
"price": {"type": "integer"},
"created_at": {"type": "date"}
}
}
}
'Now let's add a document to the index.
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/product/_doc/1?pretty -d '
{
"name": "MS T-Shirt",
"description": "Mens Summer T-Shirt",
"uom": "Piece",
"price": 299,
"created_at": "2023-01-01T10:22:33"
}
'Finally, let's validate the index and documents.
curl -X GET -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/product?pretty=true
curl -X GET -u elastic:${db_password} http://127.0.0.1:9200/product/_search?pretty=trueTo access Kibana, simply navigate to http://localhost:5601 and log in with the elastic username and password.
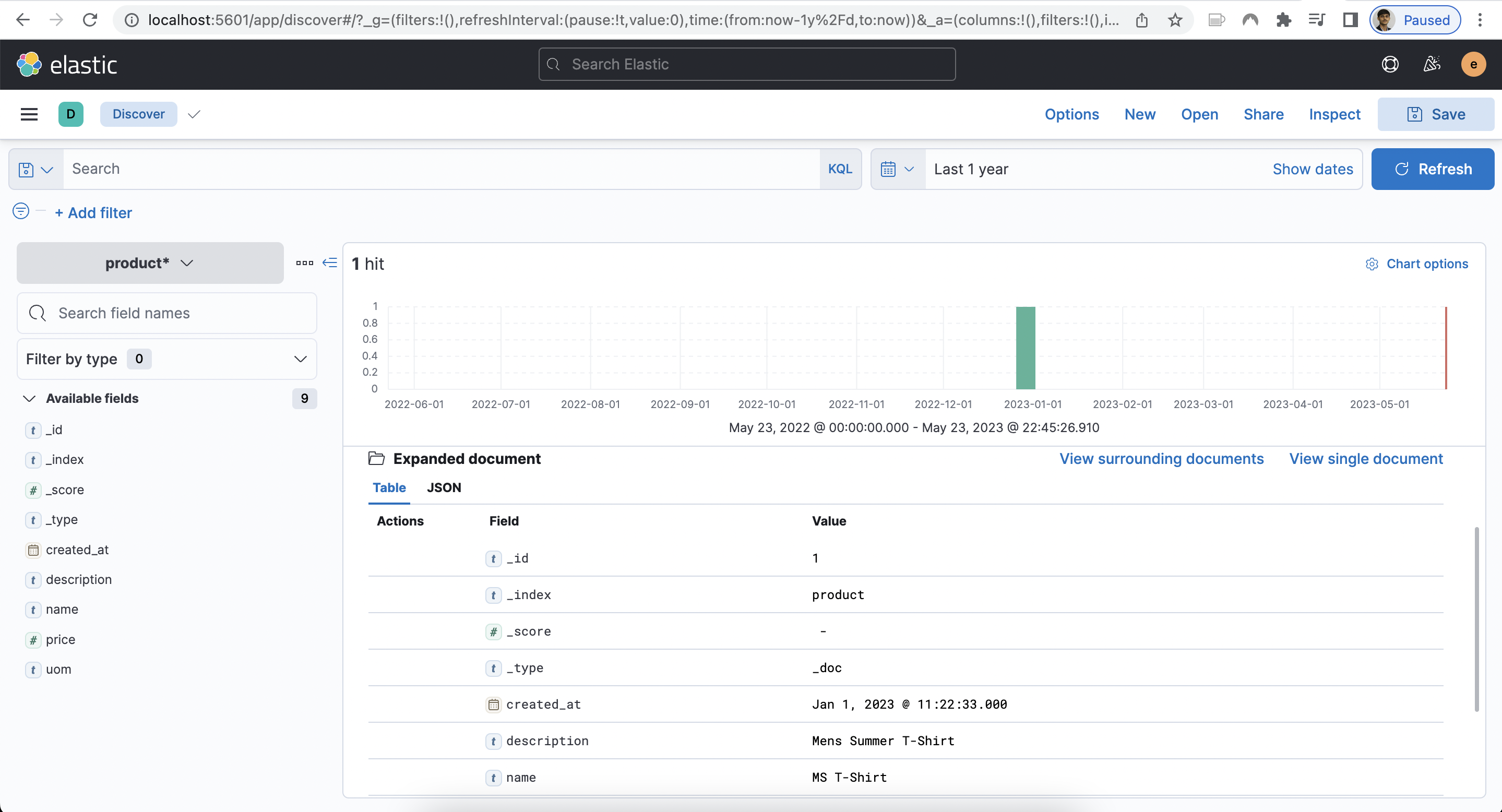
Step 5: Stop the Container
Finally, we can stop the containers by running the following command:
docker-compose -f elk-docker-compose.yml downThis will stop the containers and remove them from memory.
That's it! We've successfully created and configured a Docker Elasticsearch with Kibana containers.

